Ever feel like you're drowning in data?
You aren’t alone. The average sales rep has access to an insane amount of information from their CRM, spreadsheets, sales tools, and analytics platforms. Unfortunately, not all that data is worth your time.
Don't get me wrong, I'm not anti-data. Far from it! Understanding your data and tracking the right metrics and KPIs will help you scale your sales team, grow revenue, and crush your competition.
The trick is figuring out which data points matter and which are just noise.
I'd like to help you figure out the difference. So today, I'll share the eight sales metrics that high-performing sales teams track. Once you start prioritizing these KPIs, your sales department will become more productive and close more deals.
1. Monthly sales growth
The monthly sales growth metric measures fluctuations in sales revenue on a month-to-month basis. Tracking it gives sales managers actionable insights regarding their sales strategies.
If, for example, your company's revenue goes up every 30 days, you can safely assume your sales strategy is on point. If it goes down, you probably need to optimize your approach. Maybe a new sales process will help your reps close more deals next month.
Plenty of sales teams prioritize annual sales revenue over monthly sales growth. This is a mistake — not because annual sales revenue is a useless metric, but because monthly sales growth helps managers evaluate their departments in real-time rather than every 12 months.
Put simply, monthly sales growth will help you identify (and fix) minor problems in your sales process before they become massive issues. The same can't be said of annual sales growth.
Who benefits from this metric: This metric helps both sales managers and sales reps. Managers can use it to optimize their sales funnels, while sales reps can use it to motivate themselves to greater success in the future.
2. Calls + emails per rep
Tracking the number of calls and emails your reps make every day, week, and month is important because it helps sales managers understand what their reps do every day and whether these actions generate positive results.
Think about it: your sales reps won't close many deals if they don't talk to people. One of the easiest ways to increase revenue is to encourage reps to contact more prospects.
This isn't always the answer, however. If your reps do contact a high volume of quality leads but still aren't making enough sales, there’s a good chance your sales process is broken. You'll need to optimize it so reps can reach their quota consistently.
Who benefits from this metric: This metric is mostly for sales managers to assess individual rep performance and evaluate the effectiveness of sales strategies.
3. Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
CAC is another metric worth tracking. It specifies the amount of money it costs a company to acquire a new customer.
To calculate customer acquisition cost, use this formula: Total Costs / New Customers
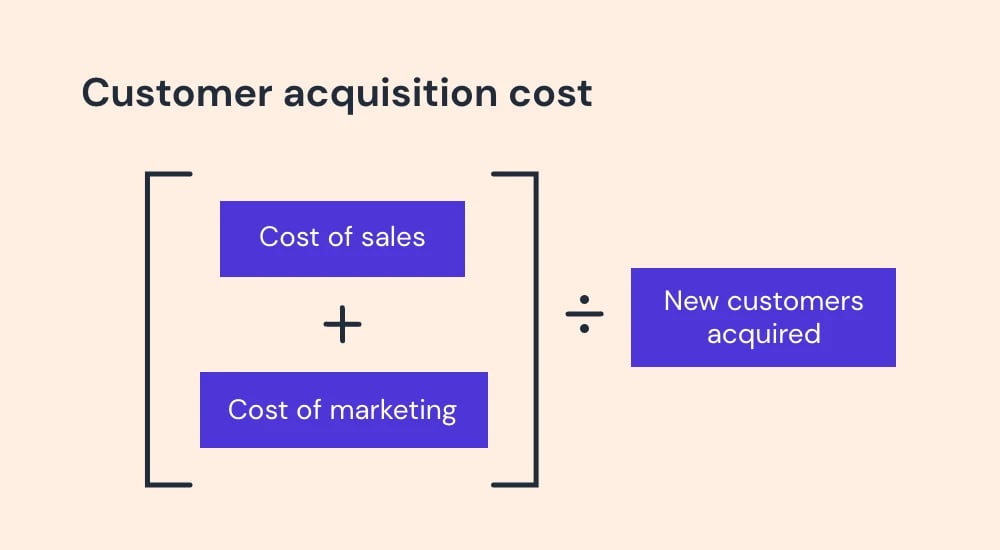
Remember, this KPI tracks every expense needed to generate a new buyer. This includes your sales rep's salary, the software tools they use to make sales, the office space your reps work in, the capital spent on marketing campaigns, and so forth.
Who benefits from this metric: Sales managers can use this metric to determine profitability. They can then devise sales strategies to reduce CAC and keep their company in the black.
4. Lead conversion rate
How many prospects actually buy a product and/or service from your company? The lead conversion rate metric is crucial to answering this question.
To find your lead conversion rate, use this formula: (Leads / Sales) x 100
Tracking this KPI is a great way to assess your sales funnel. If your lead conversion rate is lower than average, you'll know that you need to optimize your sales strategy. If, on the other hand, it's higher than average, you'll know that you can double down on your current tactics.
As long as you've trained your reps, low lead conversion rates are usually caused by poor prospecting efforts. Once you start contacting quality leads, it will likely rise.
Who benefits from this metric: Sales reps can use this metric to assess their sales pitches. And sales managers can use it to evaluate the sales strategies they've put in place.
5. MQLs to SQLs rate
MQL (aka "marketing qualified leads") refers to potential customers who meet the marketing team's idea of a good lead. SQL ( "sales qualified lead") refers to the potential customers who meet the sales team's idea of a good lead.
Surprise, MQLs don't always convert into SQLs! Marketing and sales teams often have different criteria for "good" leads, which can be an issue.
Your company can’t grow if marketing and sales teams are misaligned. The MQLs to SQLs Rate metric is important because it helps determine if the leads marketing brings in actually drive sales.
To find your MQLs to SQLs rate, use this formula: (SQLs / MQLs) x 100
Who benefits from this metric: This is an important metric for sales managers, who can use it to foster better relationships with their company's marketing team, improve lead quality, and, ultimately, boost sales.
6. New and expansion monthly recurring revenue (MRR)
MRR measures the revenue a company expects to generate every month from its current subscriber base, but there's actually more than one type of MRR.
To calculate plain MRR, use this formula: Monthly Customers x Average Revenue Per User.
Say you own a SaaS company that currently serves 1,000 active customers, and each pays an average of $34 a month to use your tool. So, your MRR is $34,000.
New MRR is calculated based on new customers. So if your company landed 10 new customers at an average of $34 per month, your new MRR is $3,400.
Expansion MRR is similar, except it tracks the growth of MRR from current customers from one month to the next, rather than new customers. For example, if you have 1,000 active customers and they paid an average of $34 in January and $44 in February, your expansion MRR would be:
[($44 – $34)/$34] x 100 = 29.4% Expansion MRR rate
MRR helps sales teams determine the effectiveness of their sales strategies. If you implement a new strategy and your MRR goes down, you'll know you need to investigate. If your MRR goes up, you can probably assume the new strategy works.
Who benefits from this metric: This is definitely a sales management metric. Department heads can use it to evaluate sales strategies and track the growth of their companies.
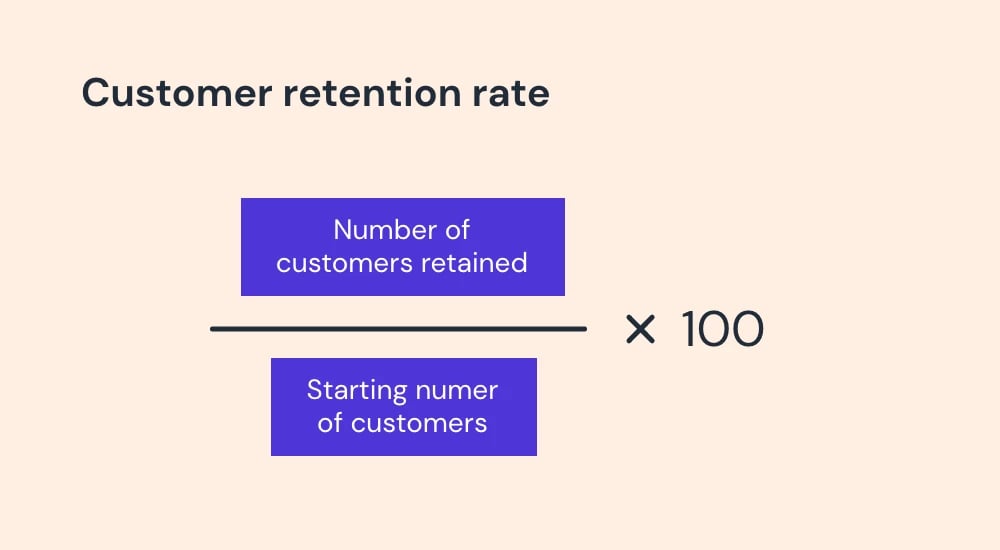
7. Customer retention rate
It costs 5x more to acquire a new customer than to retain an existing one. Moreover, a 5% bump in customer retention rate can boost profits by 25% to 95%.
In short, if you care about the profitability of your company, you need to pay close attention to your customer retention rate.
To calculate your customer retention rate, choose a time period–usually a month or a year. Then pinpoint the number of existing customers you have at the start of the period (S), the total number of customers you have at the end of the period (E), and the number of new customers you generate during the time period (N).
Then plug those numbers into this formula:
[(E-N)/S] x 100 = CRR
The higher your customer retention rate is, the better. To improve yours, make sure you sell a good product, your reps are honest with prospects, and your support team is responsive to customers. If you do these things, most of your customers will want to stick around.
Who benefits from this metric: Sales managers can use this metric to assess lead quality and customer satisfaction levels; then implement tactics to improve both.
8. Average conversion time
The average conversion time metric answers the question, "How long does it take my reps to convert a lead into a paying customer?" News flash: you want this number to be low.
Why? The lower your average conversion time is, the shorter your sales cycle will be. Short sales cycles prevent prospects from getting cold feet and help companies get paid faster.
Who benefits from this metric: This is another important sales metric for sales managers. It can help highlight issues or improvements in the department's sales funnel, assess follow-up strategies, and forecast future sales with better accuracy.
Give your sales team a boost with the right KPIs
You don't need to pay attention to every metric under the sun.
You do need to pinpoint the metrics that actually matter to your organization and track them relentlessly. Keeping up with the data will help your department achieve more success.
The question is, how do you choose the right metrics? It's pretty simple: measure actionable KPIs that align with your company's goals and fit your industry, business type, and team size. Then, choose a data platform that helps you track and analyze your data in real time.
In all likelihood, the eight sales metrics we talked about above will make your list. Good luck!